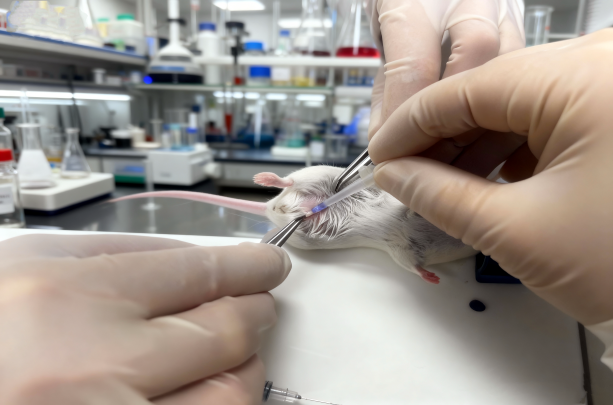
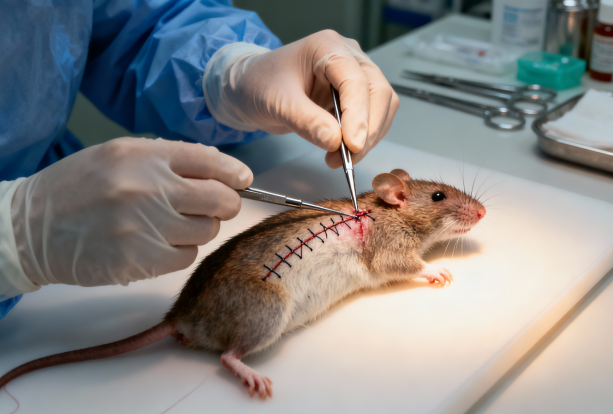
Animal testing (also known as animal experimentation) is a key link in promoting scientific research, especially in the field of oncology. Taking the mouse tumor-bearing experiment as an example, this type of research provides indispensable support for human beings to explore disease mechanisms and develop new treatment options. In most animal experiments, the experimental animals (such as mice) often need to have their wounds closed after surgery.
Traditionally, researchers use sutures or other closure methods to close wounds. They now have a new, more dependable option thanks to the development of skin glue for wound closure. This wound skin glue is a special kind of medical cyanoacrylate adhesive that can close wounds quickly and easily.
This article will explore the application effect of medical wound skin glue in animal experimental wound closure and verify whether it has better performance by comparing it with the traditional suture method.
Why Surgical Wound Closure Matters in Animal Testing?
Surgical wound closure in animal testing is of great importance, mainly in terms of meeting ethical requirements, ensuring the accuracy of experiments, maintaining the efficiency and compliance of experiments, etc.
Meet Ethical Requirements
- Reduce animal suffering: Effective wound closure reduces pain and helps animals return to normal physiology and behavior.
- Improve the survival rate of animals: In complex animal experiments such as organ transplantation and chronic disease models, the quality of wound closure directly affects the survival of animals; effective closure can avoid fatal complications such as infection and bleeding.
Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of experimental data is crucial.
- Wound healing has a direct effect on the results of experiments. For example, in mouse tumor experiments, wound infection or slow healing can trigger a systemic inflammatory response, affecting key data, such as tumor growth rate and drug metabolism, leading to distorted experimental conclusions.
- A standardized and efficient wound closure method reduces variables introduced by “wound factors,” making experimental data from different batches and samples more comparable and reproducible.
Maintaining the Efficiency and Compliance of Animal Experiments
- Some animal experimentations require multiple observations or procedures after surgery (such as tumor size measurement, blood sampling, and imaging examinations). Good wound healing can prevent wound problems from interfering with these subsequent steps, ensuring that the experimental procedure proceeds as planned.
Traditional Wound Closure Methods in Animal Testing: Limitations & Risks
Sutures (Stitching): Time-Consuming & Traumatic
The process requires specialized skills, such as threading a needle and tying knots, which demand high levels of expertise from the experimenter; it is also time-consuming due to low efficiency in experiments involving multiple tumor-bearing mice, and repeated procedures increase stress on the mice.
Stabbing: Highly irritating to the thin skin of rodents, causing inflammation and leading to poor wound healing.
Adhesive Tapes: Poor Waterproofing & Weak Hold
Adhesive tape: Prone to detachment (especially when mice are active), requiring frequent replacement, causing secondary stress, and increasing the workload of the experimenter.
Traditional wound closure methods in animal experiments face numerous challenges, including complex procedures, high stress responses, poor stability, and interference with experimental monitoring.
These challenges have prompted researchers to continuously explore more efficient, safer, and more reliable wound closure methods to improve the quality and efficiency of animal experiments.
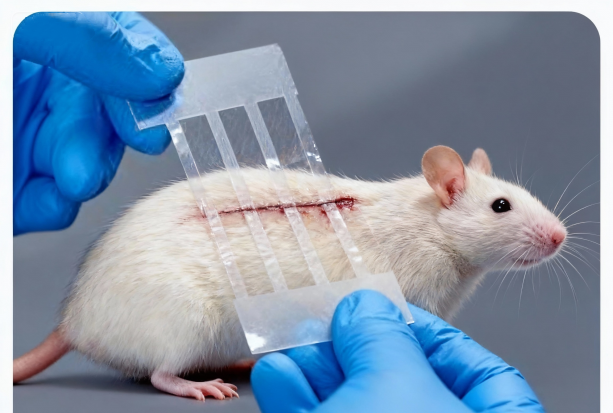
The Advantages of Skin Glue for Wound Closure in Animal Testing
Simple and Fast Operation
The application of skin glue only takes 10-15 seconds to complete the closure, which greatly shortens the wound treatment time of a single animal compared with suture (5-10 minutes).
No suture removal is required, which reduces the stress of secondary operation on animals and reduces the workload of experimenters.
Good Biocompatibility, Reduced Tissue Damage
No sutures are required, and there is no physical tissue traction or puncture damage.
Wound skin glue contains medical-grade cyanoacrylate ingredients. After the wound is glued, a waterproof and breathable film will be formed.
The film will fall off with the skin’s metabolism in 7-10 days.
Promote healing and ensure the accuracy of experimental data.
The film formed by skin glue can effectively isolate external bacteria, reduce the risk of wound infection, and promote healing.
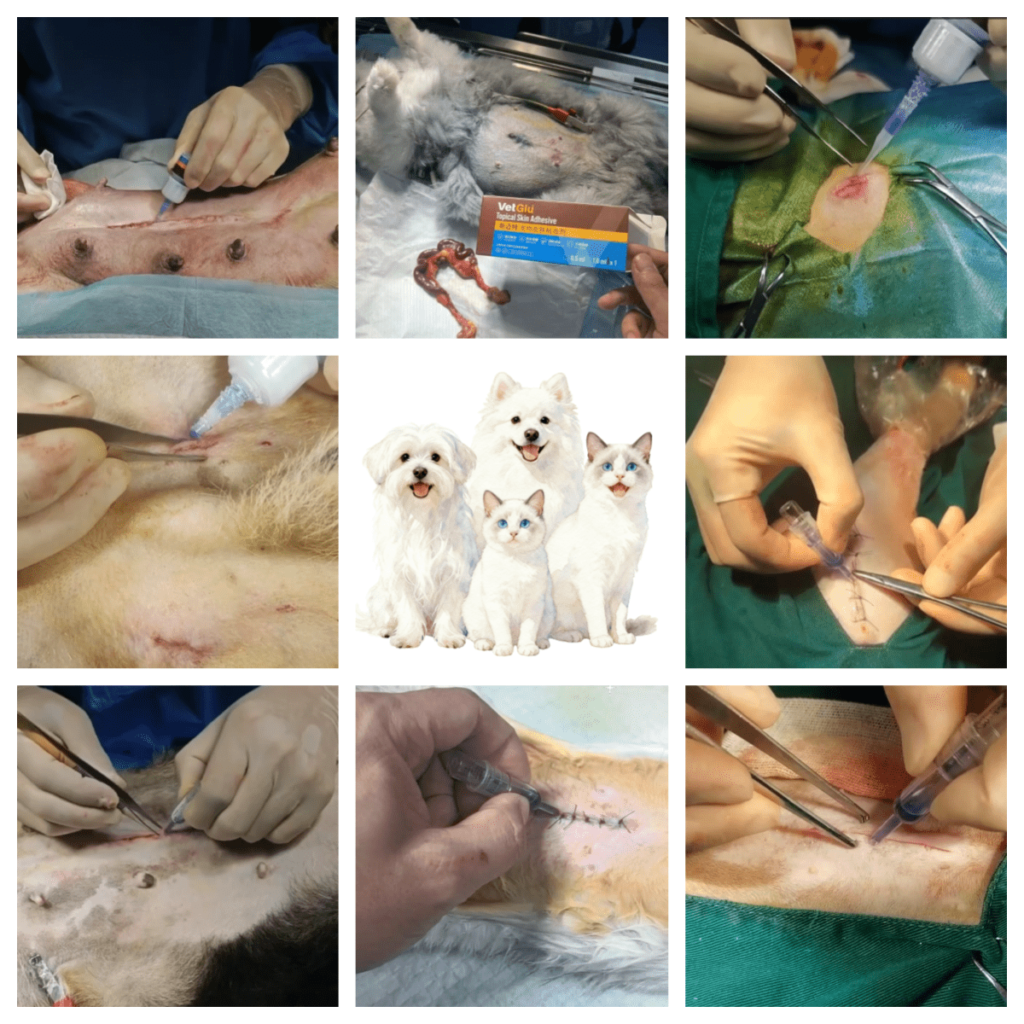
The Application of Skin Glue for Wound Closure in Mouse Tumor-Bearing Testing
The video shows researchers using VetGlu® skin glue to close wounds in a mouse tumor-bearing experiment.
In addition, in the research on the new animal model of schizophrenia in well-known universities in China, researchers used VetGlu medical-grade vet skin glue to complete the closure of the surgical wound of mice, and the feedback adhesion effect was as satisfactory as 3M VetBond tissue adhesive.
In animal experiments, the selection of skin glue is directly related to the wound closure effect, the accuracy of experimental data, and the welfare of experimental animals.
When evaluating candidate products, core indicators such as biocompatibility, cytotoxicity, bonding strength, and the closure effect should be given priority. These indicators directly determine whether the glue can avoid interfering with experimental data or causing additional tissue damage.
As a professional medical-grade skin adhesive manufacturer, we deeply understand the stringent requirements of animal experiments and veterinary scenarios.
Our skin glue has passed CE certification, which will conduct a comprehensive and strict test on the core indicators of the product, such as biocompatibility, cytotoxicity, adhesion, and bonding effect. All indicators must meet the international high standards before they can pass.
This certification is powerful proof of the product’s quality, safety, and reliability, which can make researchers and veterinarians feel at ease using it.
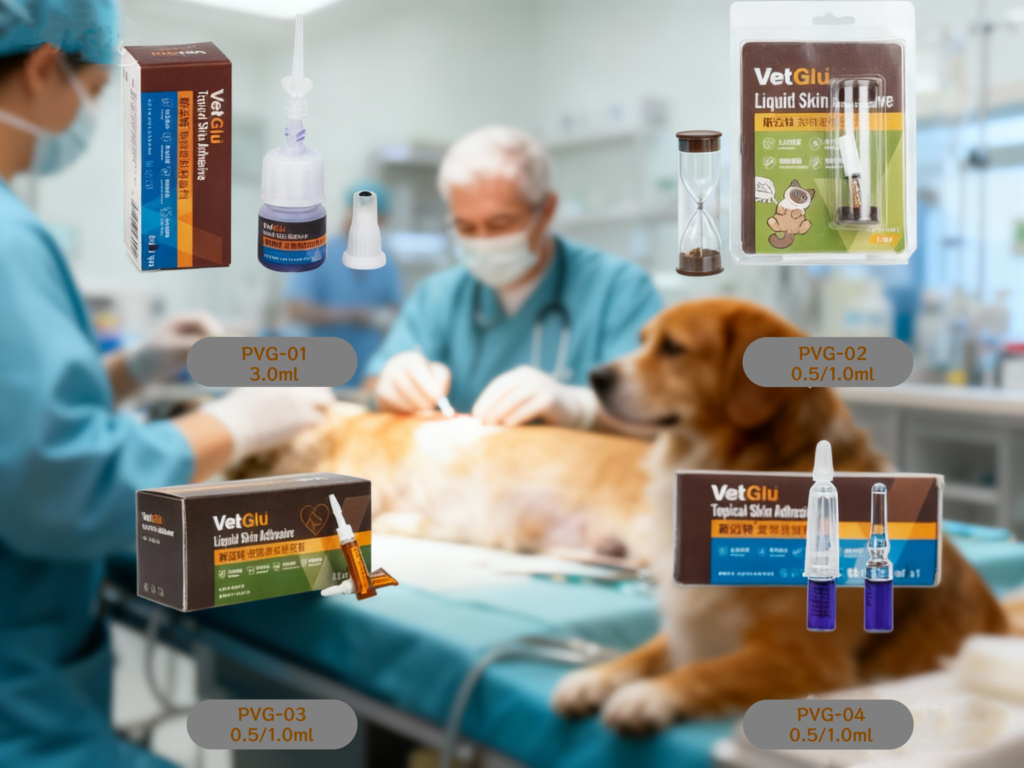
The various packaging specifications can meet the needs of local wounds in small animals and different areas in specific experiments, allowing researchers to choose flexibly and enhancing the convenience and adaptability of operations.
The 4 Types of Veterinary Skin Glue Features
Features:
- Large capacity: Suitable for treating larger wounds, economical, and cost-effective per use.
- Reusable: Large capacity, reusable multiple times, suitable for veterinary hospitals, clinics, rescue stations, and other places where vet skin adhesive is frequently needed.
- Professional quality: The bottle design is similar to 3M VetBond tissue adhesive, ensuring the professional bonding effect.
Features:
- Easy to use: Unscrew the tube and use it directly without additional tools, suitable for the daily household needs of pet owners.
- Quick adhesion: Ideal for quickly treating minor wounds in emergencies.
- Portable: Small and light, convenient for pet owners to carry when going out.

Model: PVG-03
Volume: 0.5/1.0ml
Features:
- Packaging and Sealing: Aluminum tube packaging ensures the adhesive’s freshness and extends product lifespan.
- Easy to apply: Equipped with a sponge applicator for a simple application and an improved user experience.
- Hygiene and Safety: Single-use only, reducing the risk of cross-contamination.
Features:
- Sterile packaging: suitable for strict surgical environments to ensure surgical safety.
- Suitable for High-Value Pets: Ideal for expensive pets, providing more advanced care.
- Precise Dosing: Ampoule design facilitates controlled dosage, preventing waste.
In addition to supporting scientific research, our VetGlu® skin glue is also widely used by veterinarians for routine pet surgery wound closure. If you want to intuitively understand its application effect in pet surgery, you can watch the relevant surgical video thru the following YouTuBe:
Whether you are a researcher looking for a reliable wound closure product for animal testing or a veterinarian in need of an efficient wound closure solution, VetGlu skin glue can meet your needs.
We are always committed to promoting the research and development of medical wound skin adhesives, contributing to accurate research results and high-quality animal medical care.
If you need to know the product specifications or get samples, please feel free to contact us. We look forward to supporting your work with professional knowledge and high-quality products.
REFERENCES
- João Ilgenfritz Neto 1, Ricardo Dutra Aydos 2, Iandara Schettert Silva 3, Rondon Tosta Ramalho 4, João Ilgenfritz Júnior 5, Gerson Gattats Orro de Campos 6, Ricardo Kenithi Nakamura 6, Danilo M Zanello Guerisoli 7, Wilson de Barros Cantero 8. The aplication of cyanoacrilate surgical glue on skin suture in rats. Acta Cir Bras. 2017;32(1):56-64.doi: 10.1590/s0102-865020170107. [PubMed]
- M Yaron 1, M H Erin, W Huffer, C Cairns. Efficacy of tissue glue for laceration repair in an animal model. Acad Emerg Med. 1995;2(4):259-63. doi: 10.1111/j.1553-2712.1995.tb03219.x. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hafiz Muhammad Safwan1, Ayesha Safdar Chudhary1, Muhammad Kashif Maan1, Syed Wasim Abbas1, Ghulam Abbas2* and Saad Nasir1. Comparative Evaluation of Suturing Techniques, Skin Staples and Surgical Glue for the Treatment of Auricular Hematoma in Dogs. International Journal of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Science
Volume 3, Issue 3, ISSN (Online): 2455-8567. [Google Scholar]