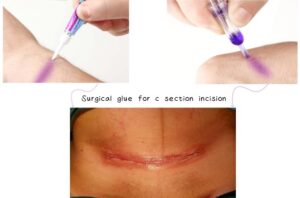
Choosing the appropriate adhesive can make a significant difference when it comes to treating cuts and wounds. Super glue and skin glue may sound alike, but they are really different. Super glue is supposed to fix objects, but skin glue is made for medical usage. If you use the wrong one, you could have big difficulties.
We’ll discuss the distinctions between skin glue and super glue in this post and why it’s crucial to apply the proper one on your wounds. If you’re a parent, a first-aid enthusiast, or just curious, knowing the distinctions can help you make better and safer choices when it comes to caring for wounds.
The key difference between skin glue and super glue
Medical skin glue and super glue are cyanoacrylate-based compounds. However, minor changes in molecular structure make one safe for skin and the other harmful.
Consider it like construction bricks: the length and kind of the blocks influence how the glue behaves on live tissue. Medical skin glue employs carefully crafted, longer chains. Superglue has significantly shorter, more reactive chains.
This seemingly minor alteration has a significant impact on how hot they become, what chemicals are released, and how your body reacts. This is the main reason why they cannot be used interchangeably.
Medical Skin Glue (Cyanoacrylate Derivatives)
Medical skin glues (like PerfectSeal® or Dermabond®) use cyanoacrylate molecules with longer chains, the main ingredient being butyl cyanoacrylate (chemical formula: C8H11NO2) or octyl cyanoacrylate (chemical formula: C12H19NO2). These longer bands connect the edges of your skin like bendy bridges. That’s important because:
- Gentle Reaction: When they touch skin moisture, they respond (polymerize) more slowly. This slow reaction generates only mild, safe heat.
- Safety: The glue film peels off naturally in 7-10 days as the wound heals; no harmful substances are produced.
- The long-chain molecules form a flexible bond that bends with the skin’s movement. This bond acts like a secure, waterproof scab that keeps out bacteria and promotes wound healing. This design has been accepted by the European Commission as safe for medical use.
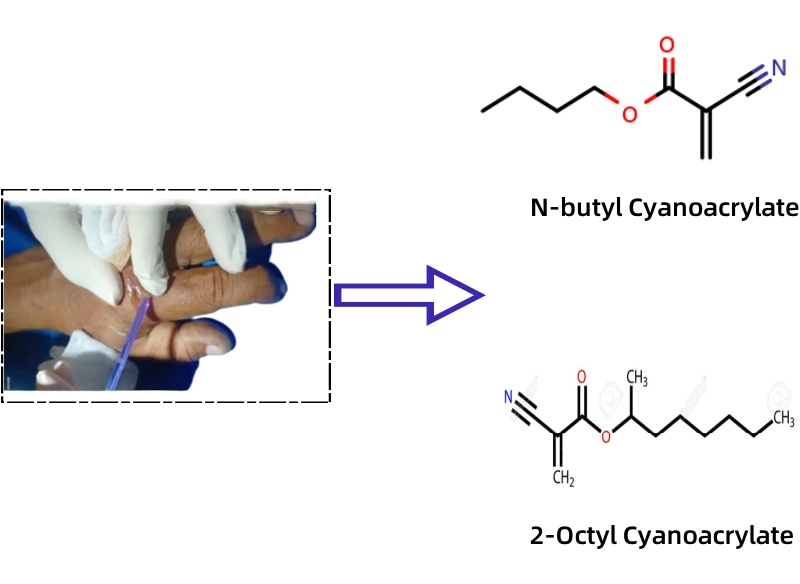
Super Glue (Home or Industrial Cyanoacrylate)
Household or industrial super glue (like Hopson Glue®, Krazy Glue®, or Gorilla Glue®) typically has as its main ingredient short-chain cyanoacrylate, like ethyl-cyanoacrylate (chemical formula: C6H7NO2). This structure makes it strong for fixing objects but dangerous for skin:
- Hot & Harsh Reaction: These short chains react instantly and violently with skin moisture. This rapid polymerization reaction creates a lot of heat, potentially causing thermal burns inside the wound.
- Toxic Breakdown: As super glue breaks down, it releases formaldehyde and other strong chemicals at high concentrations.
It is well known that formaldehyde is a colorless irritant and toxic substance that damages surrounding skin cells, causing significant inflammation and tissue damage. - Rigid & Brittle: The bond is stiff and cracks easily under skin movement, trapping bacteria and promoting infection.